In the realm of modern medicine, infusion pumps have emerged as indispensable tools for the safe and precise administration of fluids, medications, and nutrients to patients. This article explores the evolution of infusion pump technology, its impact on patient care, and the latest advancements shaping the future of healthcare delivery.
Understanding Infusion Pumps
- Introduction to Infusion Therapy: Infusion therapy involves the controlled delivery of fluids, medications, and other therapeutic agents directly into a patient’s bloodstream or body tissues. It is used in a wide range of clinical settings, including hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare, to manage various medical conditions and support patient recovery.
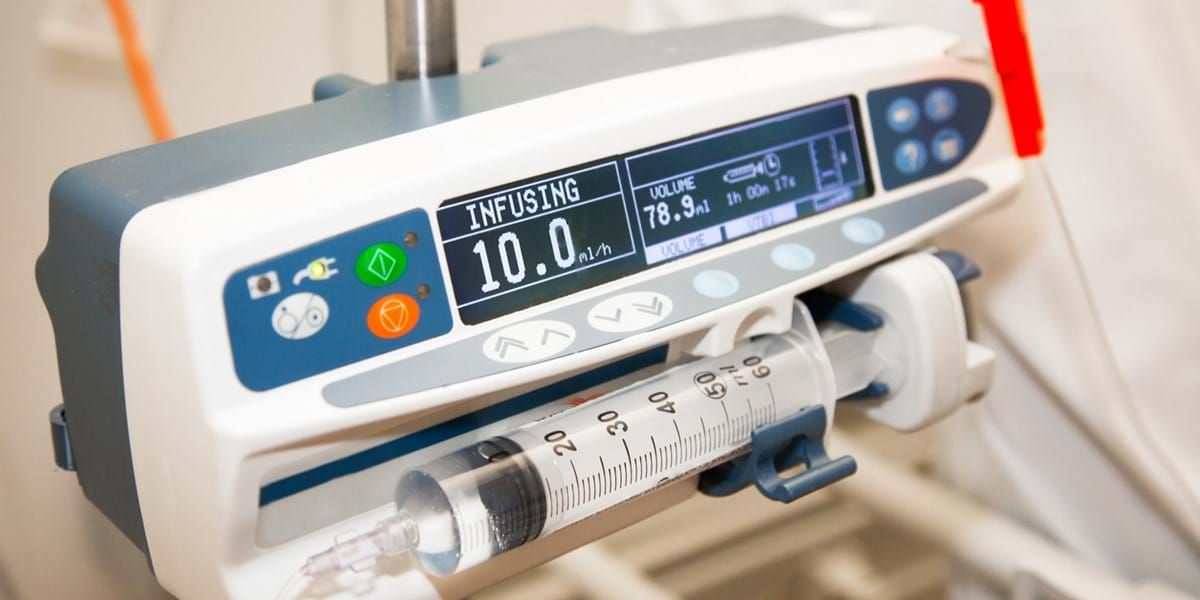
- Role of Infusion Pumps: Infusion pumps are medical devices designed to administer fluids and medications intravenously (IV), subcutaneously (SC), or epidurally (into the epidural space of the spinal cord) at a controlled and precise rate. These devices ensure accurate dosing, continuous monitoring, and enhanced patient safety during infusion therapy.
Evolution of Infusion Pump Technology
- Early Infusion Devices: The origins of infusion therapy can be traced back to ancient times, with early methods of administering fluids and medications including gravity-based drips and manual syringe pumps. These rudimentary devices lacked precision and posed significant risks of dosing errors and complications.
- Introduction of Mechanical Infusion Pumps: The development of mechanical infusion pumps in the mid-20th century represented a significant advancement in infusion therapy. These devices utilized mechanical mechanisms, such as rollers and pistons, to control the flow rate of fluids and medications, improving dosing accuracy and patient safety.
- Transition to Electronic Infusion Pumps: The advent of electronic infusion pumps in the late 20th century marked a paradigm shift in infusion pump technology. These programmable devices incorporated microprocessors and electronic sensors to deliver fluids and medications with unparalleled precision, customizable dosing profiles, and advanced safety features.
Key Features and Benefits of Infusion Pumps
- Accurate Dosing: Infusion pumps enable precise control over the flow rate and volume of fluids and medications, minimizing the risk of dosing errors and adverse drug reactions. This accuracy is crucial for administering potent medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and intravenous anesthesia, at therapeutic levels.
- Continuous Monitoring: Infusion pumps feature built-in monitoring capabilities, including alarms and alerts, to notify healthcare providers of potential issues, such as occlusions, air bubbles, or infusion site complications. Continuous monitoring enhances patient safety by facilitating early intervention and preventing adverse events.
- Customizable Dosing Profiles: Electronic infusion pumps allow healthcare providers to create customized dosing profiles tailored to individual patient needs and clinical requirements. These profiles can incorporate parameters such as infusion rate, bolus doses, and dose titration algorithms, optimizing therapeutic outcomes and patient comfort.
- Compatibility with Specialty Medications: Infusion pumps are compatible with a wide range of specialty medications, including antibiotics, chemotherapy agents, pain management drugs, and parenteral nutrition solutions. Their versatility and flexibility make them indispensable tools for delivering complex therapies in diverse clinical settings.
- Portability and Mobility: Many modern infusion pumps are designed to be portable and lightweight, allowing for easy transport and use in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, ambulatory care centers, and home environments. This portability enhances patient mobility and independence, enabling ambulatory infusion therapy and home-based care.
Applications of Infusion Pumps in Healthcare
- Intravenous Therapy: Infusion pumps are commonly used for intravenous (IV) therapy, including the administration of fluids, medications, and blood products. They play a vital role in critical care, surgery, and postoperative recovery, ensuring accurate fluid management and medication delivery to patients.
- Pain Management: Infusion pumps are utilized in pain management to deliver analgesic medications, such as opioids and local anesthetics, for acute and chronic pain control. Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps allow patients to self-administer pain medication within prescribed limits, empowering them to manage their pain effectively.
- Chemotherapy and Oncology: In oncology and chemotherapy, infusion pumps are used to deliver cytotoxic drugs and targeted therapies to cancer patients. These pumps enable precise dosing, continuous infusion regimens, and dose adjustments based on patient response, optimizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects.
- Parenteral Nutrition: Infusion pumps play a critical role in parenteral nutrition therapy, delivering essential nutrients, vitamins, and electrolytes directly into the bloodstream of patients unable to tolerate oral or enteral feeding. These pumps ensure accurate nutrient delivery and support metabolic needs in critically ill or malnourished patients.
Advancements and Future Trends
- Smart Pump Technology: The integration of smart pump technology with infusion pumps enables advanced features, such as drug library databases, dose error reduction systems (DERS), and wireless connectivity for remote monitoring and data transmission. Smart pumps enhance medication safety, streamline workflow, and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Wireless Connectivity and Integration: Infusion pumps are increasingly incorporating wireless connectivity options, allowing for seamless integration with electronic health record (EHR) systems, clinical decision support tools, and telemedicine platforms. This integration enables real-time data exchange, medication order verification, and remote monitoring of infusion therapy.
- Precision Medicine and Personalized Therapy: Advances in precision medicine and pharmacogenomics are driving the development of personalized infusion therapy regimens tailored to individual patient characteristics, genetic profiles, and treatment responses. Infusion pumps equipped with adaptive dosing algorithms and predictive analytics enable customized treatment plans and optimized therapeutic outcomes.
Conclusion
Infusion pumps have revolutionized the delivery of fluids, medications, and nutrients in modern healthcare, offering precise dosing, continuous monitoring, and enhanced patient safety. From their humble origins as gravity-based drips to sophisticated electronic devices with smart pump technology, infusion pumps have evolved significantly, shaping the landscape of clinical practice and patient care.
As technology continues to advance, infusion pumps are poised to play an even greater role in healthcare, with innovations such as smart pump integration, wireless connectivity, and personalized therapy driving improvements in medication safety, workflow efficiency, and patient outcomes. By harnessing the power of infusion pump technology, healthcare providers can continue to deliver safe, effective, and individualized care to patients across diverse clinical settings.